A Systematic Review on Clinical and Health-Related Quality of Life Outcomes following Total Gastrectomy in Patients with Hereditary Diffuse Gastric Cancer
Hui Jun Lim, Massimiliano di Pietro, J. Robert O'Neill
Cancers 2024, 16(3), 473; https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers16030473
Submission received: 2 October 2023 / Revised: 23 December 2023 / Accepted: 25 December 2023 / Published: 23 January 2024
Simple Summary
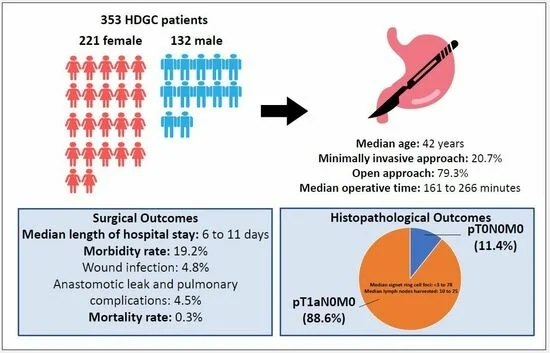
Hereditary diffuse gastric cancer (HDGC) is associated with early onset diffuse gastric cancer. Definitive treatment is surgery to remove the stomach, which has potential long-term effects on health and quality of life. As such, regular endoscopies may be offered as an alternative. This systematic review aims to evaluate outcomes following surgery for HDGC patients that will aid in patient management. Three hundred and fifty-three patients were examined in 15 studies that reported surgical outcomes. The major complication and mortality rates were 19.2% and 0.3%, respectively. Common complications included wound infection (4.8%), anastomotic leak (4.5%) and lung complications (4.5%). Following surgery, 88.6% of patients had early lesions amongst 414 patients with no lymph node involvement. There was a wide range of psychosocial effects following surgery closely related to the physical symptoms. Overall, surgery is a safe option, and it is important to be under the care of a multidisciplinary team.
Abstract
Hereditary diffuse gastric cancer (HDGC) is an autosomal-dominant syndrome associated with early onset diffuse gastric cancer. Definitive treatment is prophylactic total gastrectomy (PTG) associated with significant morbidity. Studies published from January 2000 to December 2022 reporting clinical, histopathological or health-related quality of life outcomes in HDGC patients undergoing PTG were identified. The study quality was assessed by the “Newcastle–Ottawa scale”. Of the 257 articles screened, 21 were selected. A total of 353 patients were examined in 15 studies that reported surgical outcomes. The median age was 42 years old. The median major complication and mortality rates were 19.2% and 0.3%, respectively. The most common complications were wound infection at 4.8% followed by anastomotic leak and pulmonary complications at 4.5% each. Following PTG, 88.6% of patients had early lesions amongst 414 patients. The mean/median number of signet ring cell carcinoma foci in the gastrectomy specimens was from 2 to 78. All cases were stage 1 with no lymph node involvement. There was a wide range of psychosocial effects following PTG closely related to the physical symptoms. It is imperative for patients to receive comprehensive preoperative counselling to make an informed decision and be followed up under the care of a multidisciplinary team.
23 Jan 2024















